Using proton induced monoenergetic X-ray beams at the INPP Tandem accelerator and synchrotron radiation at Elettra Sincrotrone Trieste (where the INPP group has contributed in the development and commissioning of the XRF beamline), basic research activities have been carried out with the following objectives:
1) to revisit with improved accuracy selected X-ray fundamental parameters and evaluate the reliability of existing theoretical compilations
2) to perform systematic measurements of the unknown so far X-ray Resonant Raman Scattering cross sections and
3) to study cascade-based relaxation processes and their contribution in X-ray emission.
Overall, the goal of the basic X-ray spectrometry research program is to identify the limitations of theoretical modelling of X-rays-atoms interactions and further improve the reliability of the elemental XRF analysis on any kind of material, in particular for modern advanced materials lacking appropriate reference materials
A characteristic example is presented below referring to the: “Cascade Mi (i = 1–5) subshell X‐ray emission at incident photon energies across the Lj (j = 1–3) subshell absorption edges of 66Dy”, by R. Kaur, A. Kumar, M. Czyzycki, A. Migliori, A. G. Karydas and S. Puri, X‐Ray Spectrometry. 2018;1–11, DOI:10.1002/xrs.2842. This work was accomplished through a beamtime proposal at the XRF Beamline of Elettra Sincrotrone
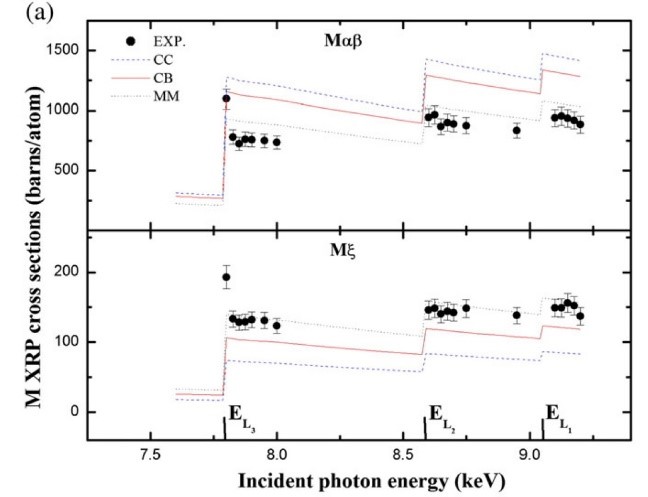
Experimental Mk (k = ξ, αβ) X‐ray production (XRP) cross sections (barns/atom) for 66Dy are compared with theoretical estimations as the function of the synchrotron induced incident X-ray beam energy
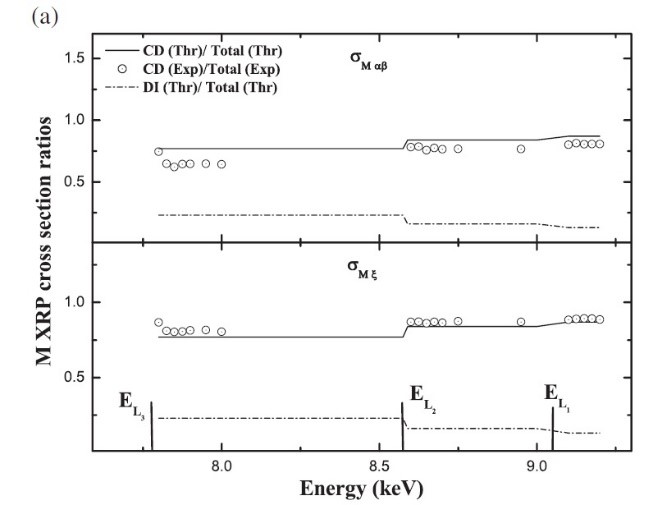
The relative contribution of the direct photoionization (DI) and the cascade decay (CD) processes to the total (DI + CD) X-ray production (XRP) cross sections for the Mk (k = ξ, αβ) X‐rays highlights the predominant contribution of cascade phenomenon for the fluorescence production of M-lines and the significant deviation from theoretical estimates.
